Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S318 - S323, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:69.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The origin of the beam non-uniformity, that is one of the key issues in large Cs-seeded negative ion sources for JT-60U and ITER, was experimentally examined by measuring correlations between the intensity of the H ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x
ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x 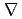 B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x
B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x 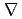 B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Inoue, Takashi; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Dairaku, Masayuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A515_1 - 03A515_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:71.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Akimoto, Hajime
Computational Fluid Dynamics 2004, p.649 - 654, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
 ion beam in a large negative ion source
ion beam in a large negative ion sourceHanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Inoue, Takashi; Morishita, Takatoshi; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.311 - 317, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Seki, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.790 - 795, 2005/08
The R&D of a 1 MeV accelerator and a large negative ion source have been carried out at JAERI. The paper presents following progress as a step toward ITER NB system. (1) Accelerator R&D: According to success in improvement of voltage holding capability, the acceleration test of H ions up to 1 MeV class energy is in progress. H
ions up to 1 MeV class energy is in progress. H ion beams of 1 MeV, 100 mA class have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m
ion beams of 1 MeV, 100 mA class have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m ), and the current density is still increasing by the ion source tuning. (2) Large ion source R&D: One of major causes that limited the NB injection performance was spatial unifomity of negative ion production in existing negative-ion based NB systems. The present study revealed that the negative ions produced in the extraction region of the source were locally destructed by fast electrons leaking through magnetic filter. Some countermeasures and their test results are also described.
), and the current density is still increasing by the ion source tuning. (2) Large ion source R&D: One of major causes that limited the NB injection performance was spatial unifomity of negative ion production in existing negative-ion based NB systems. The present study revealed that the negative ions produced in the extraction region of the source were locally destructed by fast electrons leaking through magnetic filter. Some countermeasures and their test results are also described.
Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Seki, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.790 - 795, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:59.5(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The R&D of a 1 MeV accelerator and a large negative ion source has been carried out at JAERI for the ITER NB system. The R&D is in progress at present toward: (1) 1 MeV acceleration of H ion beams at the ITER relevant current density of 200 A/m
ion beams at the ITER relevant current density of 200 A/m , and (2) improvement of uniform negative ion production over wide extraction area in large negative ion sources. Recently, H
, and (2) improvement of uniform negative ion production over wide extraction area in large negative ion sources. Recently, H ion beams of 1 MeV, 140 mA level have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m
ion beams of 1 MeV, 140 mA level have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m ). In the uniformity study, it has been clarified that electron temperature in the ion extraction region is locally high (
). In the uniformity study, it has been clarified that electron temperature in the ion extraction region is locally high ( 1 eV), which resulted in destruction of negative ions at a high reaction rate. Interception of fast electrons leaking through a transverse magnetic field called "magnetic filter" has been found effective to lower the local electron temperature, followed by an improvement of negative ion beam profile.
1 eV), which resulted in destruction of negative ions at a high reaction rate. Interception of fast electrons leaking through a transverse magnetic field called "magnetic filter" has been found effective to lower the local electron temperature, followed by an improvement of negative ion beam profile.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Masaoka, Sei; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.336 - 341, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)A microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) with a capability of track discrimination for neutron detection was developed whilst ensuring the stability of the MSGC and fulfilling the specifications required for detectors using in high-flux reactors and high-intensity pulsed-neutron sources. The developed two-dimensional detector system comprises a MSGC with individual signal channel read-outs and a new instrument system with a capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD). The InSPaD identifies the particles -proton and triton- created in the nuclear reaction 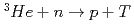 by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as
by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as 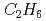 with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Kitade, Yuki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Sakurabayashi, Toru*; Imai, Naoki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Inoue, Takashi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(5), p.1760 - 1763, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)Spatial non-uniformities of extracted negative ion beam were observed experimentally in tandem-type negative ion sources. To improve the beam uniformity, it is important to analyze the plasma profile in the ion source including magnetic filter effect. In the filter region, Lorentz force is important for both ions and electrons. However, their dynamics are completely different, i.e. electrons are magnetized and ions are not magnetized. Then, the system of two-dimensional two-fluid model equations is solved simultaneously to obtain self-consistent profiles of the plasma parameters. The result shows that a possible cause of spatial non-uniformity is the ion flow rather than ExB drift motion of electrons. This flow of ions is caused by synergetic effect of the force by electric field, Lorentz force and inertia force. To verify the results above and more quantitative comparisons with experiments, full 3D analysis is needed, because the electron loss along the field line is important for the plasma potential and the electric field in the filter region. Full 3D analysis is now in progress.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Noda, Fumiaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.967 - 976, 2003/07
In J-PARC project, spallation target is irradiated by 3 GeV proton beam of 1 MW. Due to hands on maintenance for the proton beam lines, loss of proton beam is limited less than 1 W/m. Since it is difficult to predict the phase space distribution of the proton beam, we decided that the beam line have to be larger acceptance for 324  mrad, which is determined by the collimator located in the synchrotron. Distortion of proton beam is caused by the by the instability of angle at the extraction of 3-GeV synchrotron, miss alignment of the magnet, and un-uniformity of the magnet field. In this study, the distortion is calculated. In order to fit the conditions, the stability of extraction angles should be kept smaller than 0.2 mrad. As for the magnetic field, it is found that the uniformity should be kept better 5x10
mrad, which is determined by the collimator located in the synchrotron. Distortion of proton beam is caused by the by the instability of angle at the extraction of 3-GeV synchrotron, miss alignment of the magnet, and un-uniformity of the magnet field. In this study, the distortion is calculated. In order to fit the conditions, the stability of extraction angles should be kept smaller than 0.2 mrad. As for the magnetic field, it is found that the uniformity should be kept better 5x10 and 2x10
and 2x10 for bending and quadruple magnets, respectively. It is also found the error of alignments should be limited smaller than 1.0 mm and 1.0 mrad.
for bending and quadruple magnets, respectively. It is also found the error of alignments should be limited smaller than 1.0 mm and 1.0 mrad.
Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(12), p.1115 - 1119, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Makoto
Radioisotopes, 50(5), p.183 - 189, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
; *
Nuclear Technology, 122(3), p.265 - 275, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; *
Proc. of PATRAM'98, 1, p.217 - 223, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
; Nomura, Yasushi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(10), p.832 - 841, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; *
PHYSOR 96: Int. Conf. on the Physics of Reactors, 4, p.L74 - L82, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
M.Z.Hasan*; Kunugi, Tomoaki
Heat Transfer-Minneapolis,1991 (AIChE Symp. Ser. No. 283), p.67 - 73, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 151, p.202 - 208, 1988/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; Ohara, Yoshihiro;
Review of Scientific Instruments, 57(2), p.145 - 150, 1986/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:85.3(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English